- September 14, 2023
- Posted by: admin
- Categories: Software Development, Website Development

Google Cloud Services vs. AWS vs. Microsoft Azure: How to Choose Between Them
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, there are three dominant providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Each of these cloud service giants offers a wide range of cutting-edge tools, infrastructure, and features. Therefore, it’s crucial for businesses to carefully assess their requirements before committing to a specific provider. To make an informed decision, companies often engage in a thorough comparison of Google Cloud platform vs Microsoft Azure and AWS.
At QTS, our team takes a meticulous approach when selecting a cloud provider, prioritizing factors such as performance and security. Our experienced professionals are enthusiastic about sharing their expertise on these cloud providers, helping you determine which one aligns best with your needs. By the end of this guide, we’ll also share our recommendations on which provider we believe suits our needs best.
Let’s explore what these cloud giants have to offer and identify which one is the ideal fit for your requirements through a comprehensive comparison of their web services.
AWS vs Azure vs GCP: Comparing The Big 3 Cloud Platforms
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are three prominent cloud computing providers, each offering a comprehensive suite of services and tools to meet various business needs.
AWS, launched in 2002 by Amazon, is a pioneer in the cloud industry. It offers a wide array of cloud services, spanning infrastructure creation to software development. AWS was instrumental in popularizing cloud technology and introduced a pay-as-you-go pricing model based on the services used.
Microsoft Azure, formerly known as Windows Azure, is Microsoft’s cloud platform. It provides a diverse range of services that enable users to develop applications and deploy existing solutions in the cloud. Azure caters to various domains and leverages open-source technologies.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP), introduced by Google in 2011, runs on the same infrastructure as Google Search and YouTube. GCP offers services for computing, storage, and application development. Initially designed to enhance Google’s products, it has since evolved to provide customizable enterprise software development services for a broader audience.
In recent years, these three providers, AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP, have emerged as leaders in the cloud industry, as indicated in the infrastructure-as-a-service provider landscape between 2021 and 2023.
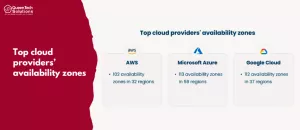
Comparison of Availability Zones in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS boasts a global presence with 32 geographic regions and a total of 102 operational availability zones. Additionally, AWS has ambitious expansion plans, aiming to introduce 15 more availability zones in five regions, including Canada, New Zealand, Israel, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Microsoft Azure:
Microsoft Azure currently operates in 59 regions, with 19 more regions in development. Within each Azure region, users can access one to three availability zones, resulting in a total of 113 operational availability zones. Furthermore, Azure is actively working on 51 additional availability zones to enhance its coverage.
Google Cloud:
Google Cloud spans across 37 regions and offers 112 operational availability zones. The company is committed to further growth, with 27 additional availability zones in development. Google Cloud’s ambitious goal is to establish a total of 133 availability zones by the end of 2024.
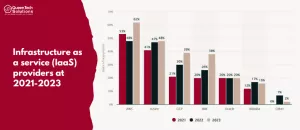
Comparison of Market Share and Growth Trends: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
When comparing Azure, GCP, and AWS, it’s essential to assess their positions and growth in the cloud market. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of these factors:
In 2023, AWS maintained its position as the leading global cloud service provider, commanding a substantial market share of 32%, down slightly from 33% at the start of the year. AWS continues to exhibit robust growth, with a year-over-year increase of 12%.
Microsoft Azure, having secured a 23% market share in 2022, emerged as the second-largest global cloud provider in 2023. Azure maintained its 23% market share early in the year and displayed impressive growth, with a remarkable year-over-year expansion rate of approximately 35%.
Google Cloud entered 2023 with an 11% market share, but this figure dipped slightly to 10% during Q1 of the same year. Nonetheless, GCP is experiencing robust growth, expanding by approximately 38% year over year.
These insights into market share and growth rates provide a comprehensive perspective on the competitive dynamics among Azure, GCP, and AWS in the ever-evolving cloud computing landscape.

Database and storage services
– AWS Storage:
Amazon Web Services provides a versatile set of cloud storage and database services known for their reliability, scalability, and security. Key storage services include:
Simple Storage Service (S3): AWS’s object storage service that allows you to store and retrieve data of any size.
Elastic Block Storage (EBS): Designed for use with EC2 instances, EBS provides persistent block storage.
Elastic File System (EFS): Offers file storage capabilities, essentially functioning as a Network File System (NFS) server.
Storage Gateway: A hybrid cloud storage service that provides access to unlimited cloud storage.
Snowball: A hardware device designed for transferring large volumes of data when internet transfer is not practical.
AWS also offers a variety of purpose-built databases, with over 15 different engines, to meet various business needs. Some of the advantages of AWS’s database services include continuous monitoring, self-healing storage, automated scaling, and enhanced security features. Popular AWS database services include Relational Database Service (RDS) and DynamoDB. For data archiving, AWS offers S3 Glacier, known for its high durability and scalability.
– Azure Storage:
Microsoft Azure provides a range of storage solutions to meet different business requirements, including:
Disk Storage: Block storage designed for business-critical applications.
Azure Blob Storage: Object storage for storing and managing unstructured data.
Files: Cloud file shares for file storage needs.
File Sync: Caching on-premises data for efficient data access.
Stack Edge: Facilitating data transfer between the cloud network and edge devices.
Data Box: A data transfer appliance for moving data in and out of Azure efficiently.
Azure’s database offerings are extensive, covering SQL, NoSQL, and specialized services for Microsoft SQL Server. Azure SQL Database is a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) SQL database, and Server Stretch Database offers hybrid storage capabilities.
– Google Cloud Storage:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a multi-regional approach to storage for enhanced availability, even during outages and hardware failures. Key storage services include:
Persistent Disk: Block storage designed for GCP compute instances.
Filestore: Network file storage for sharing data across instances.
Cloud Storage: Object storage service for storing and retrieving data.
GCP also offers Transfer Appliance, similar to AWS’s Snowball, for efficient offline data transfer.
Conclusion
Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud are the three leading cloud providers, each with its own features, strengths, and weaknesses. These companies compete by offering user-friendly services with flexible pricing while maintaining global coverage.
AWS is considered the leader, while Azure and Google Cloud focus on user-friendliness.
QTS prefers AWS for its robustness and security, as evident in our portfolio, and we’re ready to assist you in building projects that require these qualities.



